Difference between revisions of "A Step by Step Guide to Replication"
m (→STEP 1: Prepare Environment) |
m (→Step 2: Setup Export Processor (AD_SOURCE)) |
||
| Line 42: | Line 42: | ||
*'''Export Processor Type:''' Define the java class that do the real connection to ActiveMQ server. This is where the action take place. Out of the package, ADempeire only provide the connection class for Topic delivery mode, org.adempiere.process.rpl.exp.TopicExportProcessor. (once you understand more about how ActiveMQ works, you can write your own class). | *'''Export Processor Type:''' Define the java class that do the real connection to ActiveMQ server. This is where the action take place. Out of the package, ADempeire only provide the connection class for Topic delivery mode, org.adempiere.process.rpl.exp.TopicExportProcessor. (once you understand more about how ActiveMQ works, you can write your own class). | ||
*'''Export Format:''' Define what data columns of the tables (from Replication Strategy window) will be exported. ADempeire use information here to generate XML file for export. Note that, the same Export Format must be defined in TARGET as well, as ADempiere will use it to convert from XML back to raw data for import. | *'''Export Format:''' Define what data columns of the tables (from Replication Strategy window) will be exported. ADempeire use information here to generate XML file for export. Note that, the same Export Format must be defined in TARGET as well, as ADempiere will use it to convert from XML back to raw data for import. | ||
| + | *'''Client's Model Validator:''' Define the Export Model Validator and Replication Strategy. This is required only for SOURCE machine, as we want CRUD action to trigger export to ActiveMQ process. | ||
| + | === Define Replication Strategy === | ||
| + | * | ||
| + | === Define Export Processor === | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Define Export Processor Type === | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Define Export Format === | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Define Client's Model Validator === | ||
| + | |||
| + | = Step 3: Setup Import Processor (AD_TARGET) = | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | = Step 4: Validate Export & Import XML File = | ||
| + | |||
| + | = Step 5: Test Replication = | ||
| + | |||
| + | = Exploring Java Codes for Replication Module = | ||
| + | |||
| + | = Debugging Import Process Job = | ||
| + | |||
| + | = Some Issues = | ||
=See Also= | =See Also= | ||
Revision as of 23:55, 14 April 2011

Note: DISCLAIMER - This is an implementation guide written by Kittiu, from Ecosoft Bangkok, Thailand for the purpose of teaching himself while doing his own project. It is not an official guide nor meant to be comprehensive yet. Other contributors are welcome to discuss on improving it.
Contents
- 1 Overview
- 2 Message Queue
- 3 Briefing about Replication Process in ADempiere
- 4 Step 1: Prepare Environment
- 5 Step 2: Setup Export Processor (AD_SOURCE)
- 6 Step 3: Setup Import Processor (AD_TARGET)
- 7 Step 4: Validate Export & Import XML File
- 8 Step 5: Test Replication
- 9 Exploring Java Codes for Replication Module
- 10 Debugging Import Process Job
- 11 Some Issues
- 12 See Also
Overview
This page is based on the attempt to make sense of ADempiere Replication module of the author. It will be illustrated as a step by step guide for the reader to have the FEEL of what how to setup a simple Replication case between a SOURCE and the TARGET machine.
Note: This guide is based on Adempeire 360LTS and GardenWorld
Message Queue
ADempiere use Message Queue (JMS - Java Message Service Protocal) technique to integrate between systems. Using message queue has many advantage versus direct integration or webservice call. In a short word, new data from SOURCE machine will be sent to the Message Queue Server in XML format and reside there waiting for the TARGET machine to pick up. This is a more loosely couple way of integration which can guarantee data delivery regardless of the TARGET machine status during the time of delivery. And by using Message Queue Server and XML as medium, integration between different system become more simple.
Mode of Delivery
To be a bit more specific, JMS support 2 modes of delivery
- Queue: This mode is good for point to point, where there is only 1 target machine. SOURCE send message to a specified queue. TARGET receive message from that queue (and dequeue message), whenever it become available.
- Topic: This mode is good for multi cast, where there are more than 1 target machine receiving the same message. This about when we subscribe to a magazine (topic). In this approach, TARGET machines must first subscribe to a Topic. Once SOURCE send a message to that Topic, it will be boardcast to all the TARGETs. Note that, the TARGET machine must be listening during the message sending, otherwise it miss that message.
- The example in this page is based on Topic (Publish and Subscribe)
Before we move on, check out more information about ActiveMQ here
Briefing about Replication Process in ADempiere
Step 1: Prepare Environment
- Prepare 2 ADempiere 360LTS Environment, we will call it AD_SOURCE and AD_TARGET (we won't discuss how to install Adempeire here).
- Install ActiveMQ Server (See Getting Start Guide)
- Download Binary Distribution, apache-activemq-5.5.0-bin.zip from [1]
- Unzip and place the folder to C:/apache-activemq-5.5.0-bin
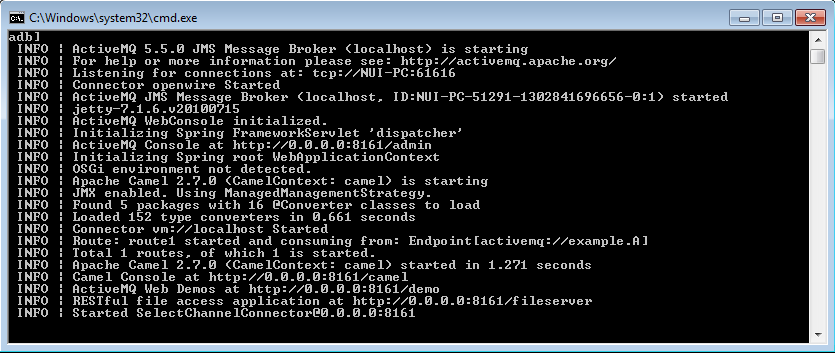
- That's it for installation, now start ActiveMQ server by running C:/apache-activemq-5.5.0-bin/bin/activemq.bat

Note: From the console, you will see that ActiveMQ
- Listening for connections at: tcp://localhost:61616 (tcp / openwire connector).
- Admin Console is at http://localhost:8161/admin. Here, we can view / manage, connection, queue, topic and etc.
- Web demo is at http://localhost:8161/demo. A good place to start off understanding ActiveMQ. And also, please check out examples code at C:/apache-activemq-5.5.0-bin/example
Step 2: Setup Export Processor (AD_SOURCE)
As mentioned earlier, the message will be sent in XML format (i.e., when a new product item is created). Beside writing your own code to generate XML file of product data and put it on the queue, ADempeire Replication Module provides windows / process to help you do just that.
- Configurations for Export
- Replication Strategy: Define what (table/document) and how, data (boardcast/reference/local/merge) will be exported. And using what Export Processor.
- Export Processor: Define where (i.e., host/port) and how (connection parameters) to connect to the ActiveMQ server. Using what Export Process Type (delivery mode).
- Export Processor Type: Define the java class that do the real connection to ActiveMQ server. This is where the action take place. Out of the package, ADempeire only provide the connection class for Topic delivery mode, org.adempiere.process.rpl.exp.TopicExportProcessor. (once you understand more about how ActiveMQ works, you can write your own class).
- Export Format: Define what data columns of the tables (from Replication Strategy window) will be exported. ADempeire use information here to generate XML file for export. Note that, the same Export Format must be defined in TARGET as well, as ADempiere will use it to convert from XML back to raw data for import.
- Client's Model Validator: Define the Export Model Validator and Replication Strategy. This is required only for SOURCE machine, as we want CRUD action to trigger export to ActiveMQ process.